Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
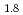 and TiH
and TiH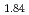 up to 21 GPa by incoherent inelastic neutron scattering
up to 21 GPa by incoherent inelastic neutron scatteringHattori, Takanori; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Iida, Kazuki*; Machida, Akihiko*; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; Honda, Takashi*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; et al.
Physical Review B, 106(13), p.134309_1 - 134309_9, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Hydrogen vibration excitations of fluorite-type ZrH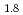 and TiH
and TiH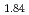 were investigated up to 21 GPa and 4 GPa, respectively, by incoherent inelastic neutron scattering experiments. The first excitation energies increased with pressure, as described by the equations
were investigated up to 21 GPa and 4 GPa, respectively, by incoherent inelastic neutron scattering experiments. The first excitation energies increased with pressure, as described by the equations 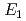 (meV) = 141.4(2) + 1.02(2)
(meV) = 141.4(2) + 1.02(2) (GPa) and
(GPa) and 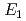 (meV) = 149.4(1) + 1.21(8)
(meV) = 149.4(1) + 1.21(8) (GPa) for ZrH
(GPa) for ZrH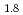 and TiH
and TiH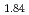 , respectively. Coupling with pressure dependence of lattice parameters, the relations between metal-hydrogen distance (
, respectively. Coupling with pressure dependence of lattice parameters, the relations between metal-hydrogen distance (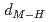 ) and
) and 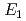 are found to be well described by the equations
are found to be well described by the equations 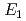 (meV) = 1.62(9)
(meV) = 1.62(9) 10
10
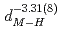 (
(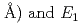 (meV) = 1.47(21)
(meV) = 1.47(21) 10
10
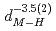 (AA), respectively. The slopes of these curves are much steep compared to the previously reported trend in various fluorite-type metal hydrides at ambient pressure. The hydrogen wave function spreading showed that the local potential field for a hydrogen atom shrinks more intensively than the tetrahedral site. These behavior is likely caused by the rigid metal ion core and the resulting confinement of the hydrogen atom in the narrower potential field at high pressures.
(AA), respectively. The slopes of these curves are much steep compared to the previously reported trend in various fluorite-type metal hydrides at ambient pressure. The hydrogen wave function spreading showed that the local potential field for a hydrogen atom shrinks more intensively than the tetrahedral site. These behavior is likely caused by the rigid metal ion core and the resulting confinement of the hydrogen atom in the narrower potential field at high pressures.
Tomimitsu, Hiroshi; Hasegawa, Yuji*; Aizawa, Kazuya
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, Vol.70, Supplement A, p.462 - 464, 2001/05
no abstracts in English
 Cu,
Cu,  Cu, Cu,
Cu, Cu,  Hg and Hg
Hg and HgTomimitsu, Hiroshi; Hasegawa, Yuji*; Aizawa, Kazuya
Physics Letters A, 274(5-6), p.175 - 183, 2000/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:42.51(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Koizumi, Satoshi; Inami, Toshiya
Macromolecules, 32(17), p.5613 - 5621, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:23.54(Polymer Science)no abstracts in English
Koizumi, Satoshi
Journal of Chemical Physics, 107(2), p.603 - 612, 1997/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:16.59(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
; *; *
Progress of Theoretical Physics Supplement, (126), p.223 - 228, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
Hattori, Takanori; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Iida, Kazuki*; Machida, Akihiko*; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; Honda, Takashi*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; et al.
no journal, ,
Recently, the high-pressure state of metal hydrides has attracted much attention due to the discovery of superhydrides with high-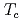 near room temperature under ultra-high pressure. The vibrational state of hydrogen is important to understand the origin of high
near room temperature under ultra-high pressure. The vibrational state of hydrogen is important to understand the origin of high 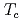 and to search for materials with higher
and to search for materials with higher 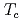 . Incoherent Inelastic Neutron Scattering (IINS) is a powerful tool to study the vibrational excitations of hydrogen. Therefore, vibrational excitations of various metal hydrides have been investigated, but a unified understanding is still lacking due to the differences in the lattice size and electronic states. Pressure allows us to investigate the nature of the lattice more rationally because the lattice size can be changed continuously. In the present work, we have developed an apparatus for IINS under high pressure, and succeeded in observing vibrational excitations of hydrogen in ZrH
. Incoherent Inelastic Neutron Scattering (IINS) is a powerful tool to study the vibrational excitations of hydrogen. Therefore, vibrational excitations of various metal hydrides have been investigated, but a unified understanding is still lacking due to the differences in the lattice size and electronic states. Pressure allows us to investigate the nature of the lattice more rationally because the lattice size can be changed continuously. In the present work, we have developed an apparatus for IINS under high pressure, and succeeded in observing vibrational excitations of hydrogen in ZrH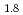 and TiH
and TiH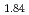 up to 21 GPa. In this talk, we will introduce the principle of IINS, the experiments, and the results obtained.
up to 21 GPa. In this talk, we will introduce the principle of IINS, the experiments, and the results obtained.
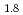 and TiH
and TiH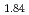 up to 21 GPa by incoherent inelastic neutron scattering
up to 21 GPa by incoherent inelastic neutron scatteringHattori, Takanori; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Iida, Kazuki*; Machida, Akihiko*; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*
no journal, ,
Hydrogen vibration excitations of fluorite-type ZrH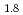 and TiH
and TiH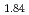 were investigated up to 21 GPa and 4 GPa, respectively, by incoherent inelastic neutron scattering experiments. The first excitation energies increased with pressure, as described by the equations
were investigated up to 21 GPa and 4 GPa, respectively, by incoherent inelastic neutron scattering experiments. The first excitation energies increased with pressure, as described by the equations 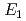 (meV) = 141.4(2) + 1.02(2)
(meV) = 141.4(2) + 1.02(2) (GPa) and
(GPa) and 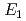 (meV) = 149.4(1) + 1.21(8)
(meV) = 149.4(1) + 1.21(8) (GPa) for ZrH
(GPa) for ZrH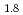 and TiH
and TiH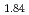 , respectively. Coupling with pressure dependence of lattice parameters, the relations between metal-hydrogen distance (
, respectively. Coupling with pressure dependence of lattice parameters, the relations between metal-hydrogen distance (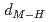 ) and
) and 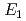 are found to be well described by the equations
are found to be well described by the equations 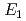 (meV) = 1.62(9)
(meV) = 1.62(9) 10
10
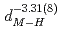 (
(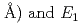 (meV) = 1.47(21)
(meV) = 1.47(21) 10
10
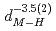 (AA), respectively. The slopes of these curves are much steep compared to the previously reported trend in various fluorite-type metal hydrides at ambient pressure. The hydrogen wave function spreading showed that the local potential field for a hydrogen atom shrinks more intensively than the tetrahedral site. These behaviors are likely caused by the rigid metal ion core and the resulting confinement of the hydrogen atom in the narrower potential field at high pressures.
(AA), respectively. The slopes of these curves are much steep compared to the previously reported trend in various fluorite-type metal hydrides at ambient pressure. The hydrogen wave function spreading showed that the local potential field for a hydrogen atom shrinks more intensively than the tetrahedral site. These behaviors are likely caused by the rigid metal ion core and the resulting confinement of the hydrogen atom in the narrower potential field at high pressures.
勅使河原 誠; 猿田 晃一
村松 一生*; 池田 裕二郎*; 大竹 淑恵*; 岩田 英里*; 高橋 一馬*; 須谷 康一*
【課題】賦形性がよく、高い放射線場での耐久性にも優れ、さらに、干渉性散乱によって冷中性子や極冷中性子を高強度化することができる、冷中性子や極冷中性子の反射材を提供する。 【解決手段】ナノ炭素構造体を含んでなる三次元形状の炭素構造体であって、前記ナノ炭素構造体はグラフェン骨格を有する20NM未満の厚さの薄片状炭素が花弁状に固定された花弁状構造、および、1~100NMの大きさのシード状構造体が集まって形成された凸凹状構造の少なくとも一つの構造を有するものである、炭素構造体。